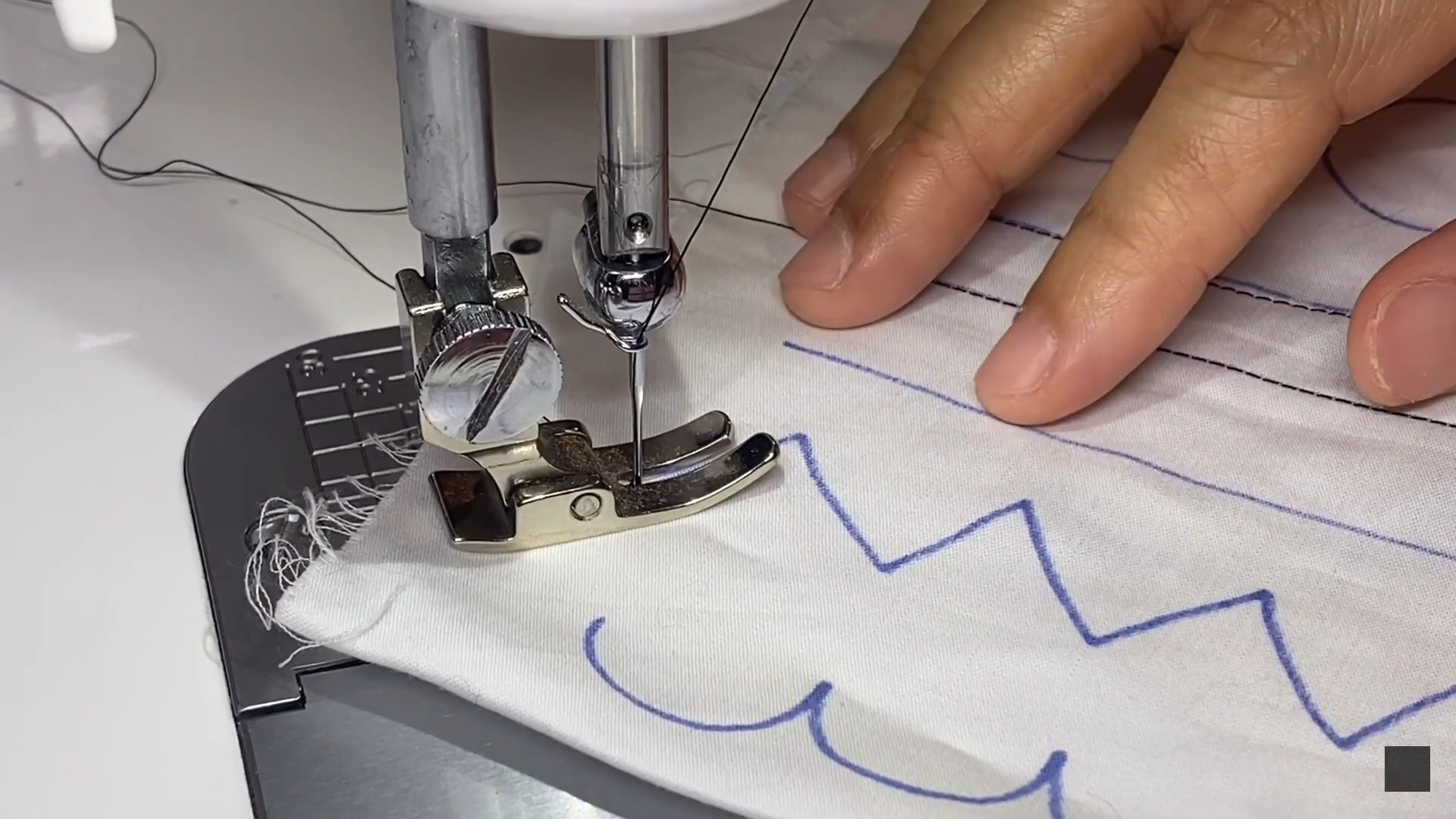
How does a Sewing Machine work? The answer you need
The sewing machine is one of the most common machineries in the 21st century.
It’s an indispensable gadget for any sewer and fabric manufacturing site, helping sewers do every basic to advanced sewing task.
So, how does a sewing machine work? Discovering more about the function and operation of a sewing machine will help you operate this device more efficiently.
I will discuss the basics of a sewing machine and give you a detailed answer.
Table of Contents
Sewing Machine Overview
The term “sewing machine” refers to any device that can sew, regardless of size, design, and special utility. These devices have appeared for a long time and have been used by many sewers in the past.
The old sewing machines are hand-operated, while most modern devices run on electricity. They feature efficient electric motors that pull a needle through many fabric garments.
These motors are the hearts of the sewing machines, which are usually covered and hidden inside the devices’ bodies. Nowadays, sewing machines come with a microchip that can perform many complicated tasks.
A sewing machine can help you with many tasks besides sewing a garment, such as turning, feeding, and feeding a fabric. Some devices even have digital displays to help sewers work more efficiently.
Read more: Who Invented the Sewing Machine?
How Does A Sewing Machine Work?
Sewing machines operate two main principles: the synchronization of fabric motion and the stitching, plus the double-threaded stitching mechanism.
The operation of a sewing machine involves a lot of motion and moving components, such as the needle, stitching, and the electric motor. All these parts must operate in synchronization to make the machine work effectively.
Therefore, it’s very hard to illustrate the operation of a sewing machine when looking at this device as a piece. I will explain each part’s working mechanism in detail to give you a more comprehensive look into sewing machines.
Before dwelling on the details, let me walk you through the core components of a sewing machine.
- Needle
- Small slots to thread the needle
- A wing nut to remove or loosen the needle
- A pressure foot
- A drawer to store sewing accessories
- The motor housing
- A hand wheel
- A selector to choose stitch type
- Stitch control
- A thread to control tension
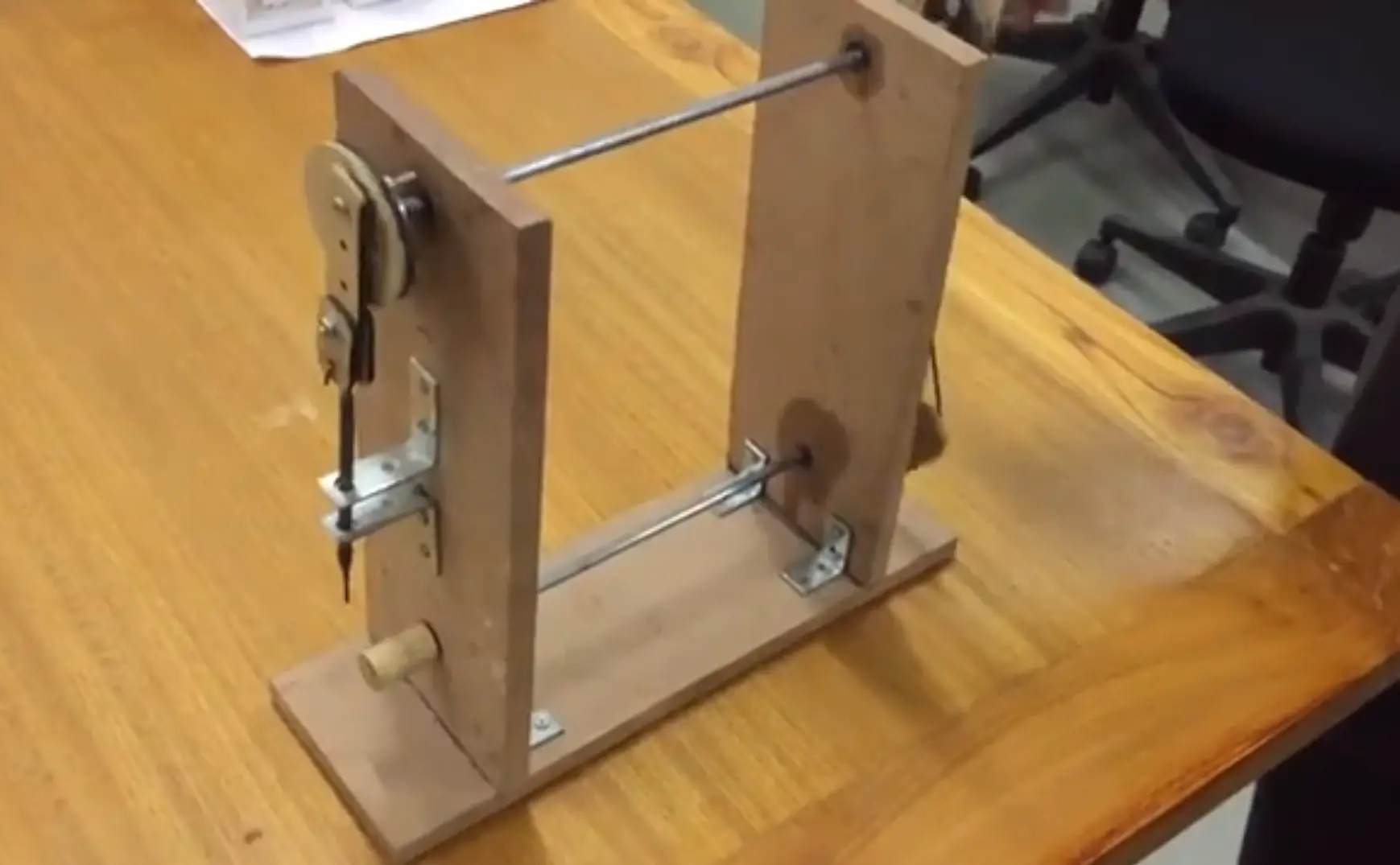

Needle Mechanism
The simple and basic mechanism of all sewing machines lies in their needles. There is a crank operated by the machine’s electric motor that moves up and down to control the needle’s motion.
Shuttle And Bobbin
The hook and shutter have to move at a faster pace than the needle to make stitches. Therefore, the crank responsible for turning the shutter has to move more quickly.
Related: Singer 3337 Review
Feed-Dog
The sewing machine’s feed dog is responsible for moving the fabric garment at an unchanged speed. This process is critical since it ensures the even length of all the stitches.
Like the needle, shuttle, and bobbin, the feed dog simultaneously features up and down motions. There are two hidden mechanisms inside the machine that control these motions.
Double-Threaded
For hand sewing, the sewers will stitch the needle through the fabric piece and pull a single thread. The sewing machine does this task much more efficiently by pricking the fabric and forming a knot before pulling through.
There is a spool thread where the needle ties through and pierces the fabric. When the needle lifts slightly, the machine will push the thread under the needle plate and form a loop.
Through the rotating hook and bobbin supply, the machine can complete a hook rotation. As a result, The sewing machine can make the knots with a second thread, and this mechanism is called double threading.
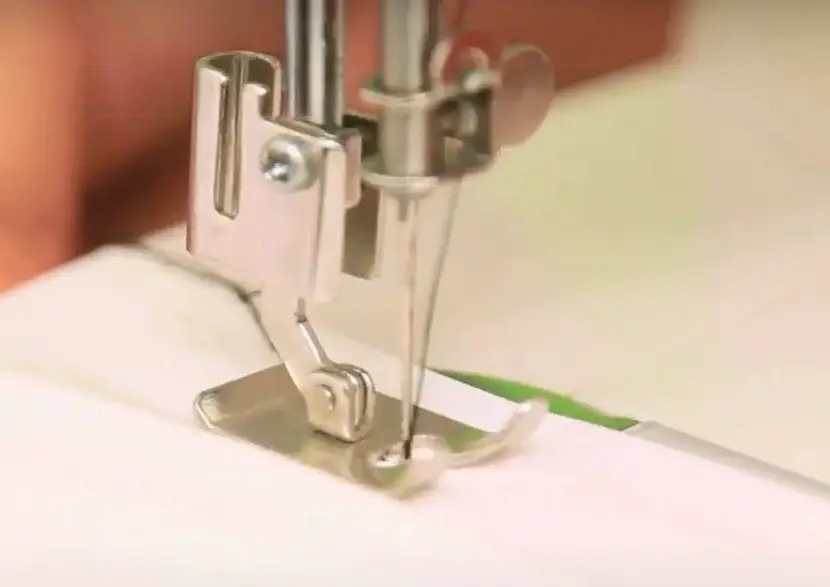

Stitch Formation
With the harmonious coordination of the mentioned components and mechanisms, a sewing machine can form beautiful and even stitches on your fabric garment.
There’s a small eye on top of the needle where sewers thread through the fabric. Meanwhile, the machine bobbin inside the shuttle will feed the bottom thread.
When the needle is stitching, a part of the stitch from the needle will form a stitch through the sewing material. When the needle punctuates the fabric and completes a stitch, it will rise up again and leave a loop.
Then, the shuttle will catch this loop and lock the thread around the bobbin. This thread gets tightened when the needle moves upward and drags it off the shuttle.
At this moment, the two threads are entirely woven into each other and make up a perfect, even stitch. This process may sound complicated, so this detailed illustration will help you figure out the stitch formation easier.
Related: What is a Walking Foot?
Who Created The Sewing Machine First?
The earliest sewing machine known to history is the work of Englishman Thomas Saint back in 1970. However, his invention still lacks many critical features that make up a functional and efficient sewing machine.
A more practical sewing machine version was credited to Elias Howe in 1946. His work features a hand crank that steadily builds up the power. The bobbin, needle, and thread also feature organized and vertical mounting positions.
In the following years, sewing machines relentlessly improved and became more efficient. There have been numerous components and improvements made to this extraordinary machine.
Similar to technological devices, the modern sewing machine is the work of countless individuals and organizations. It’s hard to credit a single individual for the fabulous device humans use nowadays.

Final Thoughts
In summary, the operation of a sewing machine is the combination of many harmonious motions from different components inside the device.
It operates mainly on the double-threaded and needle-stitching mechanisms.
Nowadays, sewing machines have become an indispensable part of the sewing industry and the lives of regular sewers. Through numerous improvements, a sewing machine can perform complicated tasks that you cannot imagine.
Though it’s not compulsory, understanding the mechanism of a sewing machine can help you utilize and maintain the device more efficiently. I hope that the answers and information provided can bring you more insights into its work.